[1] Bitar D, Lortholary O, Le Strat Y, et al. Population-based analysis of invasive fungal infections, France, 2001-2010[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2014, 20(7):1149-1155.
[2] 蔡文莹, 鲁长明, 孙九峰, 等. 130例深部真菌感染患者血液中病原菌分布及耐药性情况分析[J]. 热带医学杂志. 2013, 13(12):1480-1482.
[3] Li Y, Xu W, Jiang Z, et al. Neutropenia and invasive fungal infection in patients with hematological malignancies treated with chemotherapy: a multicenter, prospective, non-interventional study in China[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(6):5869-5876.
[4] González-Garcia P, Alonso-Sardón M, López-Bernus A, et al. Epidemiology of aspergillosis in hospitalised Spanish patients-A 21-year retrospective study[J]. Mycoses, 2021, 64(5):520-527.
[5] Zilberberg MD, Harrington R, Spalding JR, et al. Burden of hospitalizations over time with invasive aspergillosis in the United States, 2004-2013[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1):591.
[6] Pham D, Howard-Jones AR, Sparks R, et al. Epidemiology, Modern Diagnostics, and the Management of Mucorales Infections[J]. J Fungi (Basel), 2023, 9(6):659.
[7] von Lilienfeld-Toal M, Wagener J, Einsele H, et al. Invasive Fungal Infection[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116(16):271-278.
[8] Salazar F, Bignell E, Brown GD, et al. Pathogenesis of Respiratory Viral and Fungal Coinfections[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2022, 35(1):e0009421.
[9] Sharma B, Nonzom S. Mucormycosis and Its Upsurge During COVID-19 Epidemic: An Updated Review[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2023, 80(10):322.
[10] Schauwvlieghe AFAD, Rijnders BJA, Philips N, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2018, 6(10):782-792.
[11] Hoenigl M, Seidel D, Sprute R, et al. COVID-19-associated fungal infections[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2022, 7(8):1127-1140.
[12] Dam P, Cardoso MH, Mandal S, et al. Surge of mucormycosis during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Travel Med Infect Dis, 2023, 52:102557.
[13] Feys S, Almyroudi MP, Braspenning R, et al. A Visual and Comprehensive Review on COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA)[J]. J Fungi (Basel), 2021, 7(12):1067.
[14] Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, et al. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: the SEIFEM-2004 study[J]. Haematologica, 2006, 91(8):1068-1075.
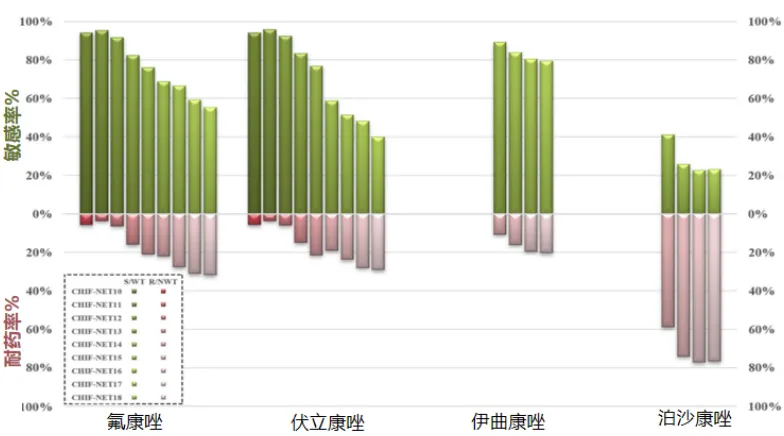
[15] Xiao M, Chen SC, Kong F, et al. Distribution and Antifungal Susceptibility of Candida Species Causing Candidemia in China: An Update From the CHIF-NET Study[J]. J Infect Dis, 2020, 221(Suppl 2):S139-S147.
[16] Wang Y, Fan X, Wang H, et al. Continual Decline in Azole Susceptibility Rates in Candida tropicalis Over a 9-Year Period in China[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12:702839.
[17] Yang X, Chen W, Liang T, et al. A 20-Year Antifungal Susceptibility Surveillance (From 1999 to 2019) for Aspergillus spp. and Proposed Epidemiological Cutoff Values for Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus: A Study in a Tertiary Hospital in China[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12:680884.
[18] Chamilos G, Luna M, Lewis RE, et al. Invasive fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies in a tertiary care cancer center: an autopsy study over a 15-year period (1989-2003)[J]. Haematologica, 2006, 91(7):986-989.
[19] 中国医药教育协会真菌病专业委员会,国家皮肤与免疫疾病临床医学研究中心(北京大学第一医院),国家血液疾病临床医学研究中心(北京大学人民医院). 侵袭性真菌病实验室诊断方法临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61(2):134-141.
[20] Schauwvlieghe AFAD, Rijnders BJA, Philips N, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2018, 6(10):782-792.
[21] Patterson TF, Thompson GR 3rd, Denning DW, et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2016, 63(4):e1-e60.
[22] Ullmann AJ, Aguado JM, Arikan-Akdagli S, et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2018, 24 Suppl 1:e1-e38.
[23] 中国医师协会血液科医师分会, 中国侵袭性真菌感染工作组. 血液病/恶性肿瘤患者侵袭性真菌病的诊断标准与治疗原则(第六次修订版)[J] . 中华内科杂志, 2020, 59 (10):754-763.
[24] Koehler P, Bassetti M, Chakrabarti A, et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: the 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2021, J21(6):e149-e162.
[25] Cornely OA, Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Arenz D, et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of mucormycosis: an initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in cooperation with the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2019, 19(12):e405-e421.
[26] Warris A, Lehrnbecher T, Roilides E, et al. ESCMID-ECMM guideline: diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis in neonates and children[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2019, 25(9):1096-1113.
[27] 中国成人念珠菌病诊断与治疗专家共识组. 中国成人念珠菌病诊断与治疗专家共识 [J] . 中华传染病杂志, 2020, 38 (1):29-43.
[28] 叶先平, 朱美英, 刘璐璐, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病并发侵袭性肺曲霉病诊治策略. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2019, 18(4):392-395.
[29] NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Prevention and Treatment of Cancer-Related Infections. Version 3. 2022.





 后可发表评论
后可发表评论



 公众号
公众号
 客服微信
客服微信