登录方式
方式一:
PC端网页:www.rccrc.cn
输入账号密码登录,可将此网址收藏并保存密码方便下次登录
方式二:
手机端网页:www.rccrc.cn
输入账号密码登录,可将此网址添加至手机桌面并保存密码方便下次登录
方式三:
【重症肺言】微信公众号
输入账号密码登录
注:账号具有唯一性,即同一个账号不能在两个地方同时登录。

BACKGROUND
Little is known about the inpact of ECMO on PK, antibiotic administration is challenging.
Available data are actually limited to animals, simulated ex-vivo, or small retrospective human studies.
Amikacin has good bactericidal activity against pseudomonas aeruginosa and low resistance rate.
Antibacterial effect of amikacin is determined by Cmax/MIC ( optimal antibacterial activity obtained with 8-10).
Amikacin Cmax range should be 60-80mg/L.(法国指南推荐>60mg/L,中国药品说明书56-64mg/L).
An amikacin dose of 25 mg/kg TBW, only 67-72% of ICU patients have been found to achieve that objective.
PURPOSE
To determine the frequency and identify factors predictive of insufficient amikacin Cmax in critically ill patients on ECMO.
To analyze the probability of attaining the established PK target ( 68-80mg/L).
METHODS
Prospectively included all consecutive patients from 2015-1 to 2016-2.
Intravenous amikacin loading dose on VV or VA ECMO.
Only the first dose was studied.
Exclusion criteria.
Incorrect amikacin regimen (<23 or="">27mg/kg TBW ).
Incorrect time of amikacin infusion( ±5 min ).
Incorrect time ( ±5 min ) or absence of Cmax determination.
Incorrect time of Cmin determination( ±1h ) were excluded if Cmax had been obtained correctly.
Amikacin: 25mg/kg TBW, diluted in 50mL of 0.9% NaCl, infused over 30 min.
Weight >120 kg, amaximum of 120 kg was the loading dose ( 5 ).
Cmax 30min after infusion ended.
Cmin 24 h after infusion ended.
Fluorescence-polarization immunoassay to determine amikacin concentrations, as a routine procedure available 24h/day, 7 days/week.
METHODS —data collection
Demographic data.
Simplified acute physiology score (SAPS) II.
Reason for ECMO.
ECMO-membrane duration “the delay between membrane first use and the time of amikacin infusion”.
Organ dysfunction an inclusion.
SOFA score.
Laboratory tests.
Inotrope score [DA+NE+E dose(γ/kg/min)]*100.
24-h fluid balance=intake-output over 24 h before infusion.
Proteinemia and hematocrit changes = (X0h – X24h)/(X0h + X24h)/2.
Renal function KDIGO classification, ARF = KDIGO ≥ 2.
Infection sites and pathogens.
RESULTS
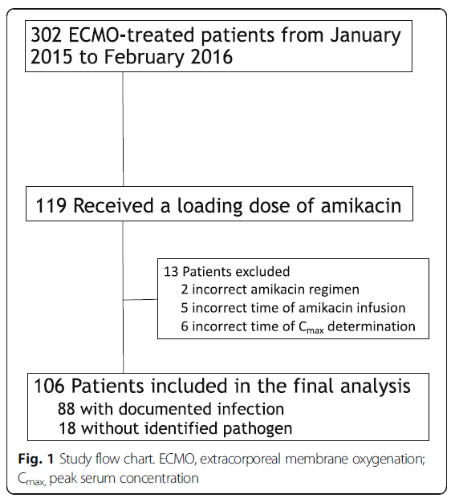
39% recevied amikacin loading dose
Infection sites: lung 77%, cannula 14%.
Pathogens: P. aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp. , escherichia coli.
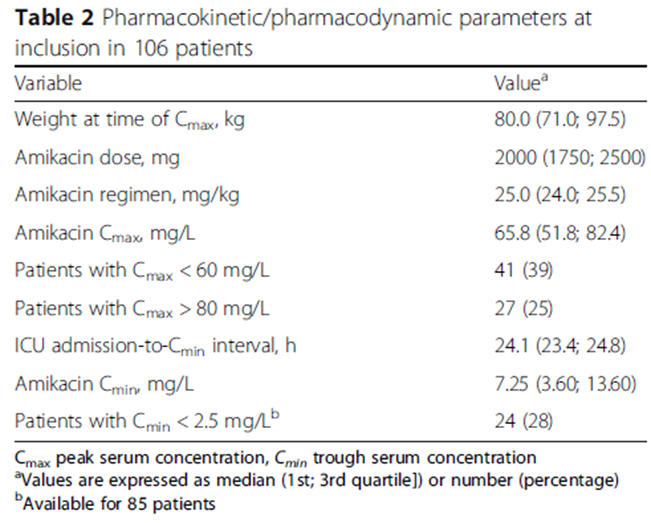
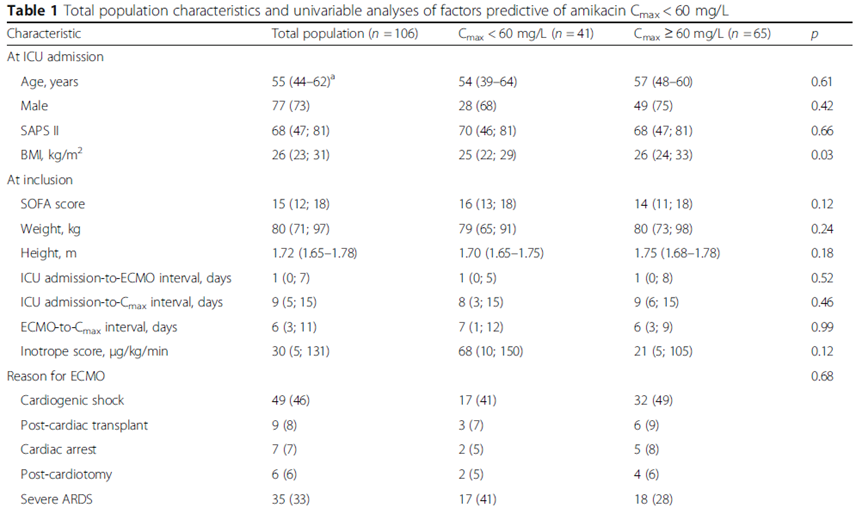
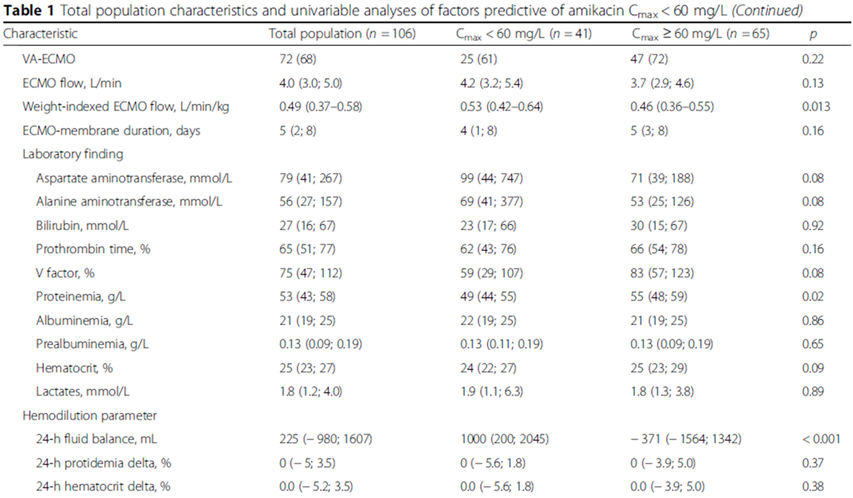
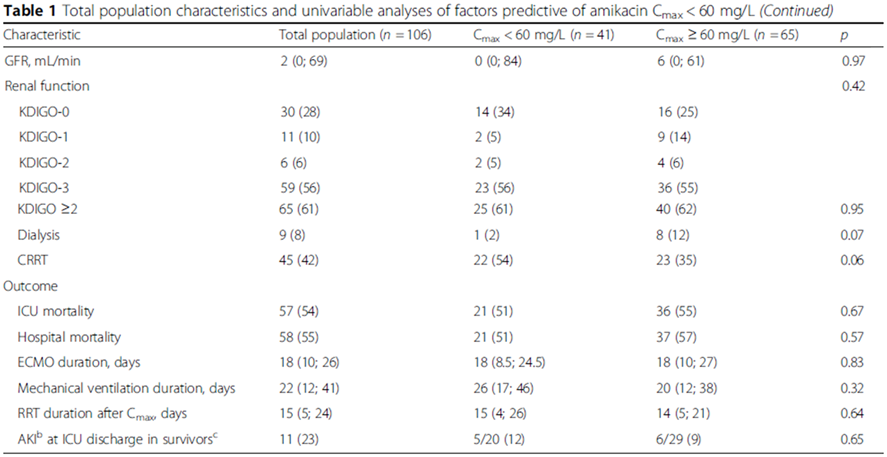
Factors predictive of Cmax<60 mg/L
Univariable analyses selected: BMI, higher AST or/and ALT, lower proteinemia, lower HCT, positive 24-h fluid balance.
Multivariable analyses: independently associated with a higher risk of Cmax < 60mg/L.
BMI < 22 kg/m2(OR, 6.38; 95% CI, 1.79-22.77; p=0.043).
24-h fluid balance(OR, per 550-mL increment, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.65; p=0.041).
出入量和Cmax < 60mg/L风险呈线性相关。
Probability reached > 60% when 24-h fluid balance exceeded 2000mL.
未发现Cmax < 60mg/L和ECMO种类、流量、膜持续时间相关。
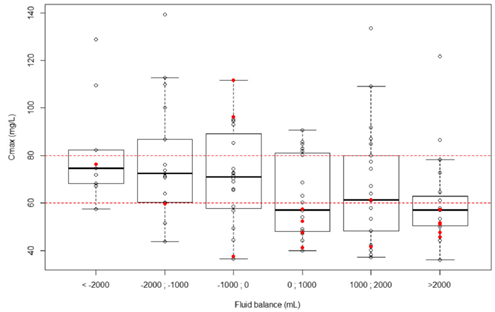
Factors predictive of Cmax>80 mg/L
Univariable analyses: higher BMI, ECMO flow, dialysis, higher HCT.
24-h fluid balance was forced into the logistic regression.
Multivariable analyses: independently associated with a higher risk of Cmax > 80mg/L.
BMI > 22 kg/m2(OR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.03-1.18; p=0.0037).
Dosing Simulations
根据测量的Cmax和药物公斤体重剂量,根据文献,假设阿米卡星PK是线性的,以模拟其他药物剂量时的Cmax。
出入量正平衡患者增加amikacin剂量至30mg/kg,可能降低低峰浓度风险至28%。
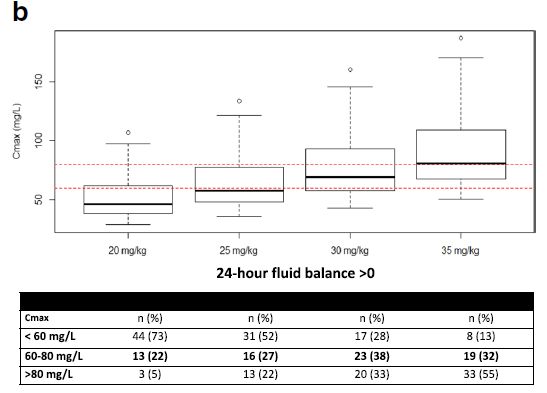
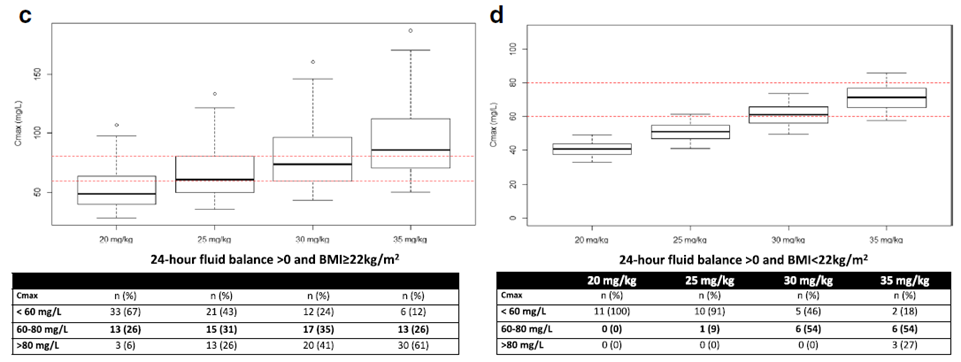
当增加amikacin至30-35mg/kg,出入量正平衡,BMI无论是多少,42%患者可能达到靶峰浓度,23%患者可能amikacin峰浓度仍不足。
OUTCOME
Mortality 54%。
11 survivors AKI,与非AKI患者相比Cmax无明显差。
ICU mortality和不足的Cmax或过高的Cmin无明显相。
ICU mortality在Cmax<60,60-80,>80之间无明显差异(59%,52%,51%)。
DISCUSSION

146例重症患者,其中15%为ECMO患者。
33%患者Cmax不足60mg/L。
预测Cmax不足的独立危险因素:BMI<25kg/m2及24小时出入量正平衡。
ECMO患者,膜肺、入量多、疾病严重都会引起Vd增加,但本研究与重症患者药物浓度不足比例相似。
46例ECMO患者的队列研究发现,与非ECMO的重症患者相比,阿米卡星Cmax不足的比例相当。
作者推测,重症患者因sepsis、低白蛋白血症、低胶体渗透压,血管内液体向组织间隙中转移增加,最终可增加药物的Vd。

低BMI是Cmax不足的预测因素,与既往报道一致。
高BMI与Cmax >80mg/L独立相关,高BMI患者使用实际体重剂量可能高估阿米卡星的Vd。
体重和阿米卡星的Vd相关性较差,因此调整肥胖患者的体重,譬如理想体重或调整体重,可能会有不同的结果。
LIMITATIONS
单中心,ECMO患者多,不能代表其他中心。
ECMO患者是VV、VA混合,基础病及预后均不相同,若根据基础病做亚组分析应有意义,但本研究多因素分析在亚组中不能找到预测峰浓度不足的因素。
合并用药也可能对AKI造成影响。
剂量模拟基于阿米卡星线性PK,其中出入量正平衡、BMI低亚组患者少,仅有11人。
不能除外阿米卡星附着在ECMO膜上。
CONCLUSIONS
使用ECMO治疗的重症患者,当阿米卡星25mg/kg体重使用时,1/3患者药物峰浓度不足60mg/L。
在低体重及出入量正平衡的ECMO患者中,增加阿米卡星剂量至35mg/kg,可能达到足够的药物峰浓度,需进一步研究。
文献原文下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iEm0JixuLDl8QVJm8oDSGQ
提取码:ebj9
 后可发表评论
后可发表评论

相关推荐
1
mNGS联合常规微生物检测可缩短ICU内SCAP的临床改善时间!詹庆元教授团队发表全球首个mNGS临床应用前瞻性随机对照研究
4835
2
文献学习46|mNGS在肺部感染应用中的进展及思考(二)
3490
3
文献学习53|宏基因组二代测序在肺部真菌感染诊断中的应用:肺活检与支气管肺泡灌洗液比较
3222
4
文献学习7 | ICU超声肌肉评估
3181
5
文献学习28 | 重症监护室获得性衰弱
3152
6
文献学习45|mNGS在肺部感染应用中的进展及思考(一)
2917
7
文献学习37 | 经皮膈肌电刺激系统在机械通气患者应用的初始评估
2820
8
文献学习12 | 肌松剂在ARDS中的早期应用
2464
9
文献学习23 | 利奈唑胺与万古霉素治疗ICU患者气管导管MRSA生物膜的疗效比较
2430
10
ARDS免疫精准诊断和治疗之困惑、挑战和策略
2230


友情链接
联系我们
 公众号
公众号
 客服微信
客服微信