登录方式
方式一:
PC端网页:www.rccrc.cn
输入账号密码登录,可将此网址收藏并保存密码方便下次登录
方式二:
手机端网页:www.rccrc.cn
输入账号密码登录,可将此网址添加至手机桌面并保存密码方便下次登录
方式三:
【重症肺言】微信公众号
输入账号密码登录
注:账号具有唯一性,即同一个账号不能在两个地方同时登录。
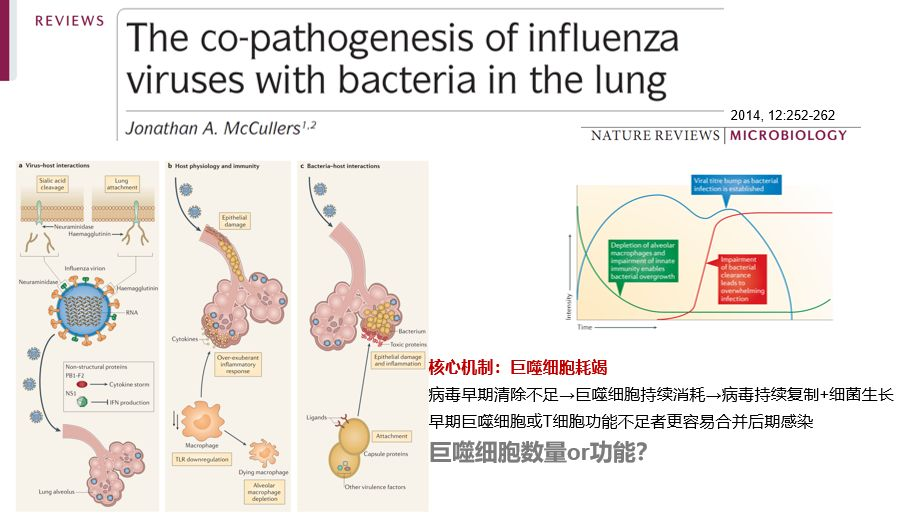
导语:新型H1N1甲型流感病毒导致的重症肺炎是高致死性疾病,但近百年来我们所获得的临床资料显示,重症流感导致患者死亡的主要原因是严重的继发感染,流感病毒增加细菌感染的易感性,病情常进展迅速,因此被称为super-infection。在β内酰胺类抗生素广泛应用的今天,甲流后继发MRSA感染成super-infection中最常见的病原菌。研究证实,继发于病毒感染的多种免疫细胞功能抑制是细菌感染的重要原因。关于单核-巨噬细胞、淋巴细胞在流感病毒感染过程中数量和功能的动态变化一直是流感免疫在研究重点。在感染早期,多种免疫细胞呈现出过度激活,介导细胞因子过量释放,而感染后6-7天,则呈现为免疫耗竭状态,对细菌、真菌清除能力下降。这些基础研究成果帮助我们更好的认识重症流感后super-infection的免疫机制,为危重患者super-infection的预警和救治提供了新的思路。
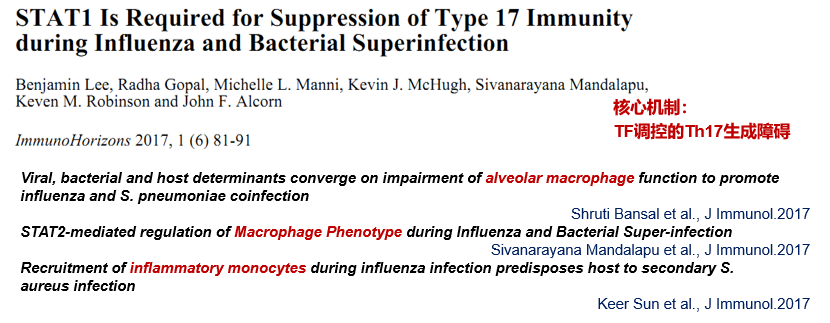
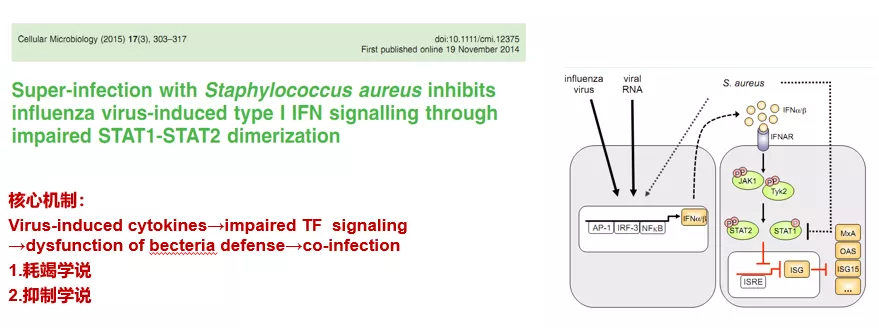
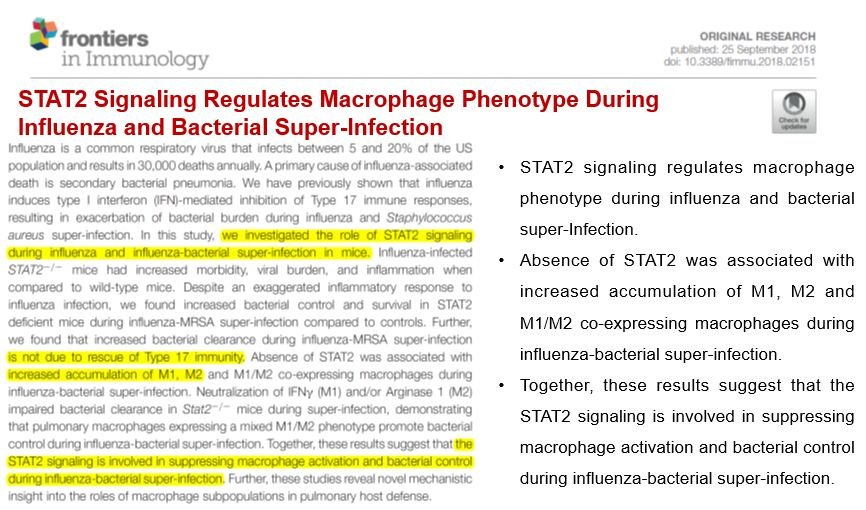
该研究团队之前已经证明流感病毒通过I型干扰素介导Th-17免疫反应水平下调,导致流感期间细菌清除能力下降,进而发生MRSA肺炎。在本项研究中,该团队在H1N1甲型流感病毒感染后继发细菌感染的小鼠模型中研究了STAT2通路的作用。STAT2基因敲除(STAT2-/-)小鼠与野生型(WT)小鼠相比,在流感病毒感染早期有更强烈的炎症反应,但在继发细菌感染时,STAT2-/-小鼠肺内细菌清除及存活率均较野生型增加。STAT2-/-小鼠在super-infection过程中,肺内M1、M2型巨噬细胞数量均增加,同时出现共表达M1和M2分子标志物的巨噬细胞亚群。当使用IFN-γ(M1型细胞因子)和/或Arg-1(M2型细胞因子)的中和抗体后,STAT2-/-的保护作用削弱了。表达混合M1/M2表型分子标志物的肺巨噬细胞亚群促进细菌清除,是STAT2信号途径在super-infection过程中发挥保护作用的机制。由此可见,STAT2信号参与了流感病毒感染后巨噬细胞活化和细菌清除过程。该研究揭示了流感病毒感染宿主后不同时期肺内巨噬细胞亚群分化特点,阐明了STAT2调控巨噬细胞分化在super-infection的细菌防御中的新机制。
这一研究成果能帮助我们筛查甲流患者中super-infection的高危人群,并提示我们如果能在重症流感患者中选择合适的时机靶标性调控巨噬细胞分化,可能减少继发感染风险。
Background—super-infection
Influenza A viruses: severe respiratory failure—morbidity and mortality
Secondary pneumonia: co-infection (super-infection)
1918/1919 pandemic: more than 95% of fatal cases can be traced back to a secondary bacterial pneumonia— S. pneumoniae.
1957/1958 and 1967/1968 pandemic: S. aureus
2009 H1N1(Within the last decades): MRSA
Aspergillus: another potential agent of super-infection
Mechanism of Co-infection
Innate immunity
Cell Differentiation and Function
Mechanism of Co-infection
Innate immunity
Transcription factors regulate cell differentiation and function
Introduction
Innate immune system
production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines→
type I (IFN α/β) ,type II (IFN γ) and type III interferons (IFNλ) →
phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2 downstream→
Type I, type II and type III IFNs have been shown to have important roles during influenza infection.
STAT1 and STAT2 were crucial for viral control and survival.
Innate immune system
production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines→
type I (IFN α/β) ,type II (IFN γ) and type III interferons (IFNλ) →
phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2 downstream→
Type I, type II and type III IFNs have been shown to have important roles during influenza infection.
STAT1 and STAT2 were crucial for viral control and survival.
Introduction
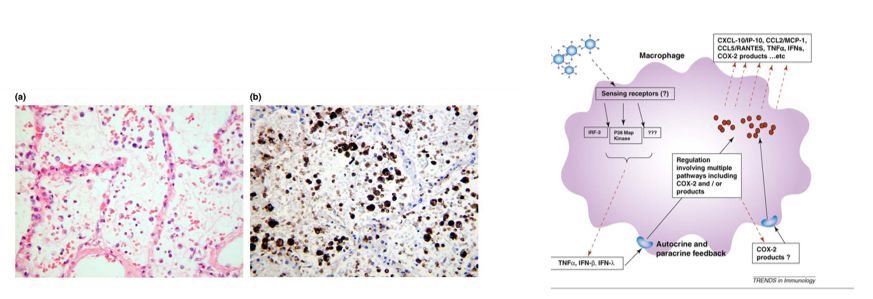
CD68+ macrophage
Neutrophils drive alveolar macrophage IL-1β release during respiratory viral infection .Thorax 2017;0:1–11.
Immune Impairment of Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytosis During Influenza Virus Pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):778-82.
Question
the role of macrophage during influenza infection and influenza-bacterial super-infection
the role of STAT2 signaling in macrophage differentiation
Results
Influenza Severity Is Increased in Stat2−/− Mice Compared to WTInfluenza Severity Is Increased in Stat2−/− Mice Compared to WT
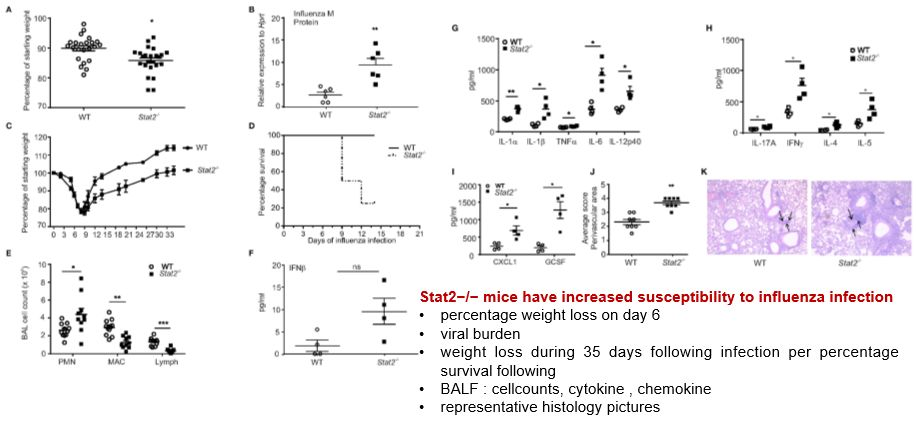
Results
Stat2−/− Mice Are Rescued From Impaired Bacterial Clearance During Influenza/ MRSA Super-Infection
Co-infection model:WT or Stat2−/− mice were infected with 100 PFU of influenza for 6 days then challenged with 5 × 107 cfu of MRSA for one additional day
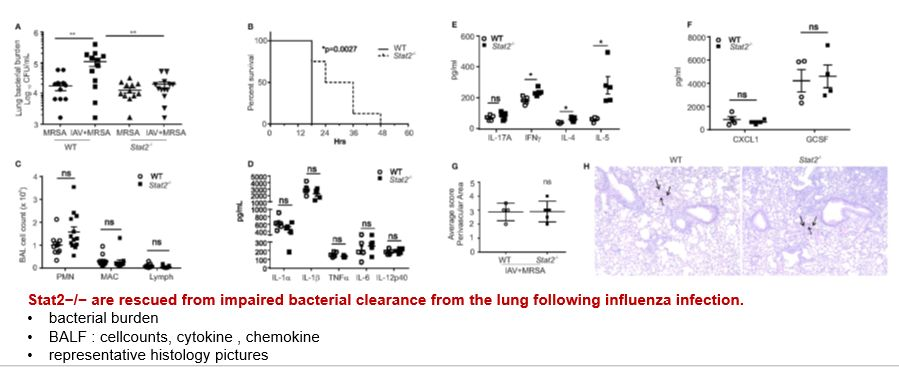
Results
Rescue of Bacterial Clearance in Stat2−/− Mice Is Associated With M1 and M2 Signature in Infected Lungs.
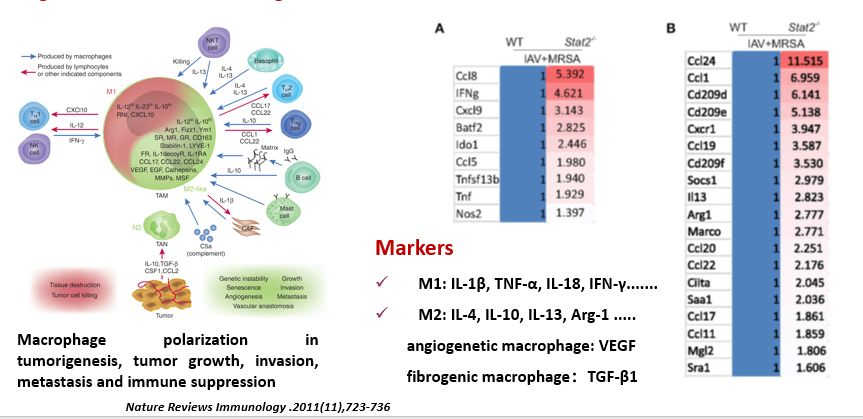
Results
Rescue of Bacterial Clearance in Stat2−/− Mice Is Associated With M1 and M2 Signature in Infected Lungs
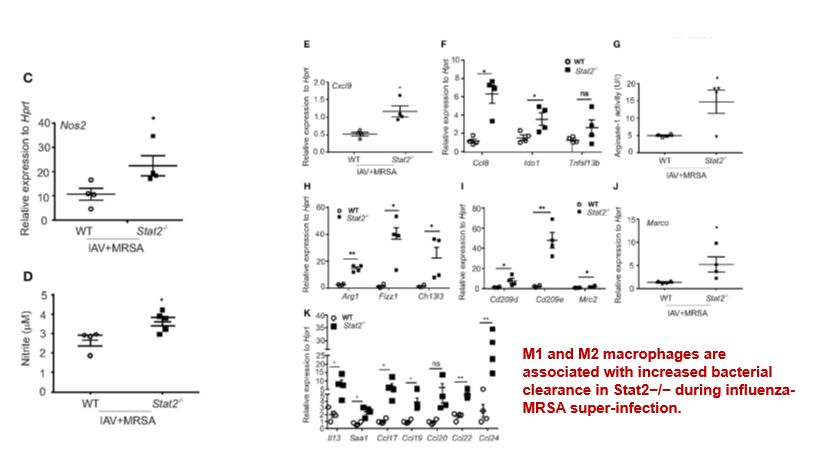
Results
Rescue of Bacterial Clearance in Stat2−/− Mice Is Associated With M1 and M2
Signature in Infected Lungs
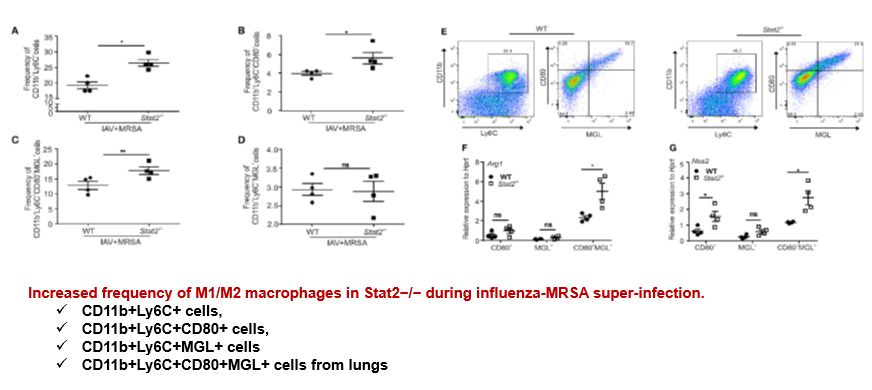
Results
Increased Accumulation of M1 and M2 Macrophages in Stat2−/− Mice Is Dependent on Preceding Influenza Infection.
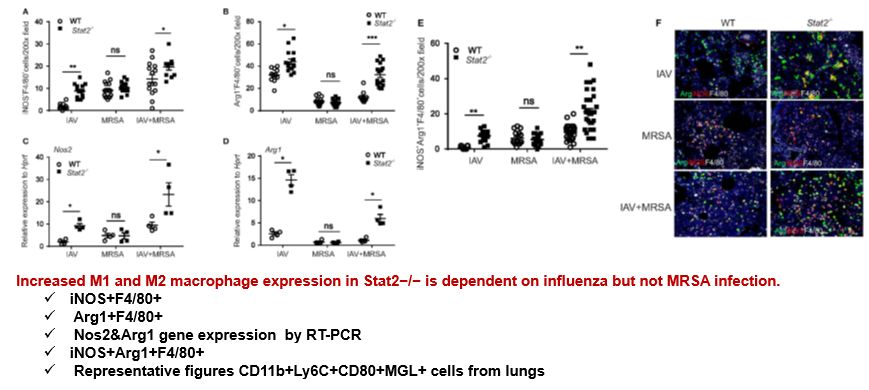
Results
Dual Function M1/M2 Macrophages Are Required for Control of Bacterial Burden in Stat2−/− Mice
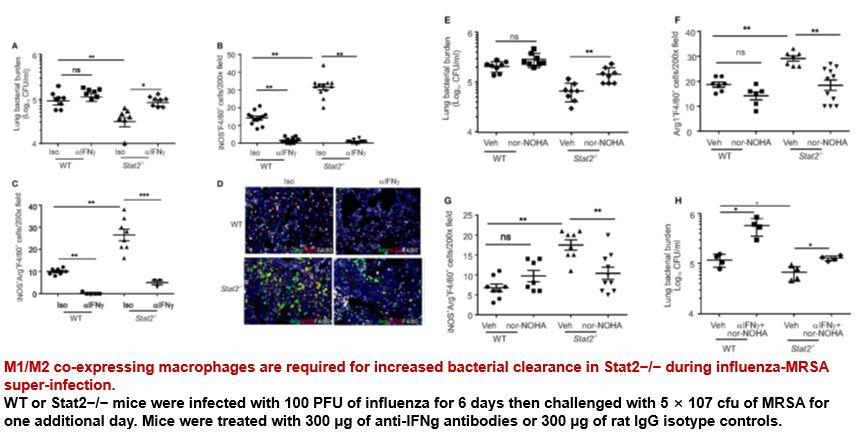
Results
STAT2 Signaling Negatively Regulates Macrophage Bacterial Uptake and Killing
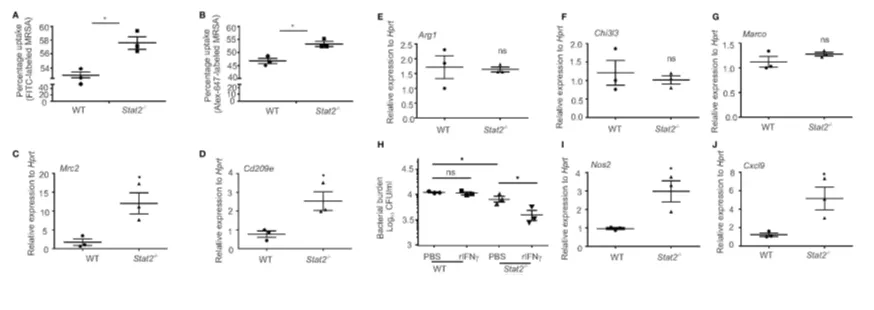
Increased bacterial uptake and killing efficiency in BMDMs from Stat2−/− mice BMDMs were generated and infected with FITC or Alex-647-labeled MRSA for 30min.
Results
Contribution of Hematopoietic or Stromal Cell Compartments in Stat2−/− Mediates Improves MRSA Clearance in Super-Infection
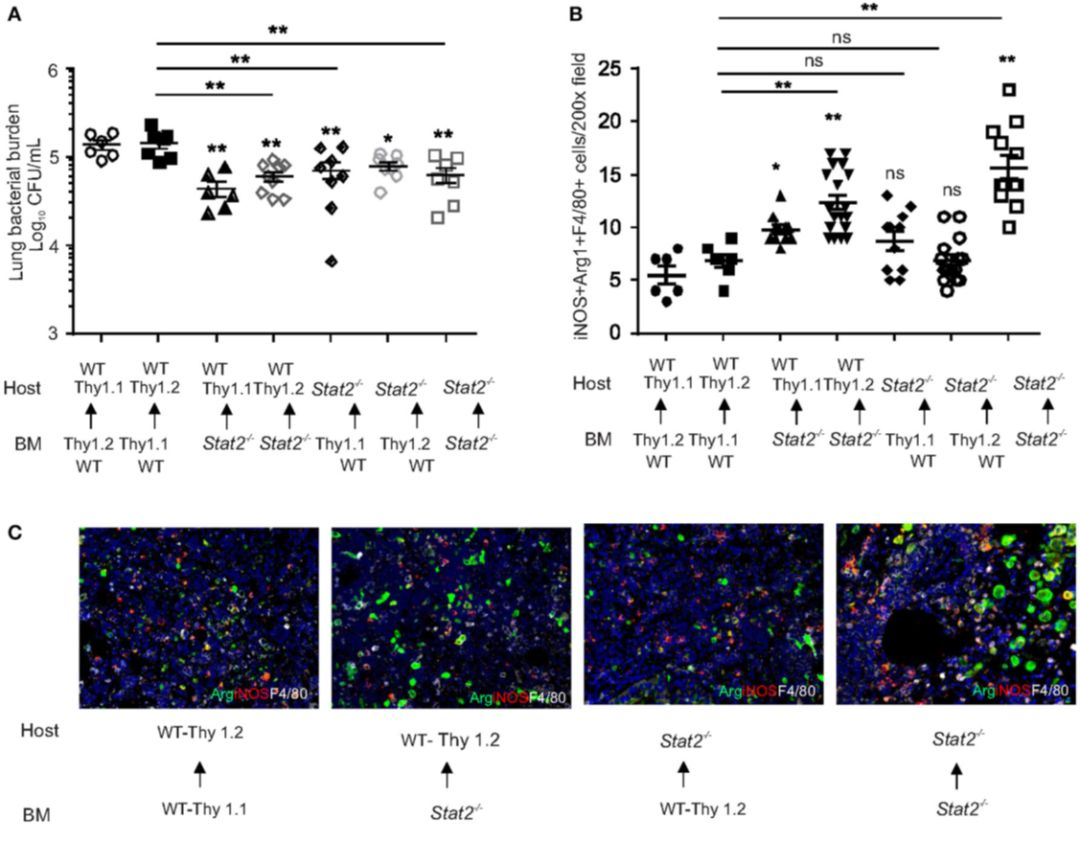
Results
Contribution of Hematopoietic or Stromal Cell Compartments in Stat2−/− Mediates Improves MRSA Clearance in Super-Infection
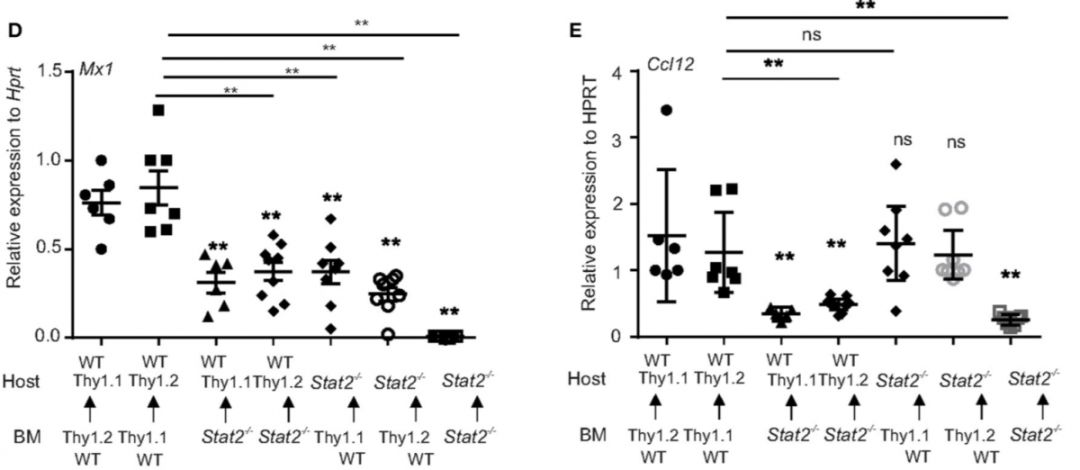
Increased bacterial control in cells from hematopoietic or non-hematopoietic compartments of Stat2−/− mice.
WT BMC (Thy1.1 host, Thy 1.2 BM or Thy1.2 host, Thy 1.1 BM),
Stat2−/− BMC (Stat2−/− host, Stat2−/− BM)
Hematopoietic Stat2−/− BMC mice (Thy 1.1 or Thy 1.2 host, Stat2−/− BM),
nonhematopoietic Stat2−/− BMC (Stat2−/− host, Thy 1.1 or Thy 1.2 BM)
Discussion
STAT2 signaling decreases influenza viral burden and inflammatory immune responses during influenza infection, at the cost of inhibiting bacterial control during subsequent bacterial challenge.
STAT2 signaling plays its role by suppressing a distinct M1/M2 dual function macrophage population during influenza-bacterial super-infection.
These data show a novel role of influenza induced type I IFN-mediated STAT2 signaling in inhibiting bacterial control through suppression of macrophage activity during influenza and influenza/MRSA super-infection.
STAT2 and dual function M1/M2 macrophage activation may be a potential target for the treatment or prevention of influenza-bacterial super-infection.
Exhausted CD8+ T cell
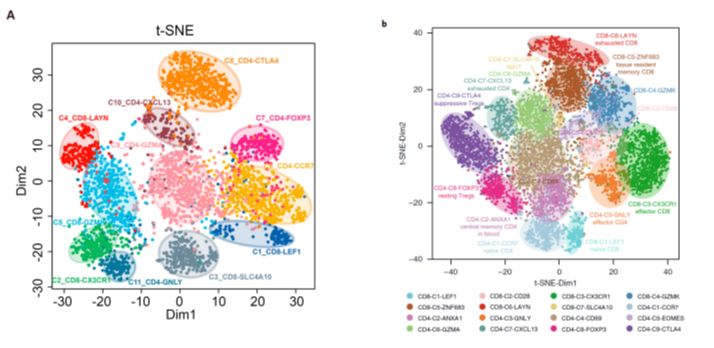
Global characterization of T cells in non-small-cell lung cancer by single-cell sequencing
Nature Medicine. 2018(24): 978–985
Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing
Cell .2017(169) :1342–1356
Hypothesis
Based on this information and considering that
我们猜测在甲流病毒感染下气道后,招募到肺的巨噬细胞表现为耗竭性亚型,当细菌或真菌感染后,增加了super-infection,如果能在合适的时机靶标性调控巨噬细胞分化,可能减少继发感染风险。
对耗竭性巨噬细胞亚型占优势的患者,预防性治疗。
Evaluation
临床实验
二次感染病例
检测IVA后合并感染者STAT1/STAT2表达
检测IVA后合并感染者巨噬细胞数量和表面Marker
super-infectionM1/M2数量和比例
血清及BALF IFN-g及TNF-a释放水平
Immunological Disorders
Upon IAV infection, the proportion and number of myeloid cells in the lungs change markedly.
neutrophil, monocytes-macrophage, monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs)
 后可发表评论
后可发表评论

相关推荐
1
mNGS联合常规微生物检测可缩短ICU内SCAP的临床改善时间!詹庆元教授团队发表全球首个mNGS临床应用前瞻性随机对照研究
4770
2
文献学习46|mNGS在肺部感染应用中的进展及思考(二)
3416
3
文献学习53|宏基因组二代测序在肺部真菌感染诊断中的应用:肺活检与支气管肺泡灌洗液比较
3184
4
文献学习7 | ICU超声肌肉评估
3137
5
文献学习28 | 重症监护室获得性衰弱
3118
6
文献学习45|mNGS在肺部感染应用中的进展及思考(一)
2885
7
文献学习37 | 经皮膈肌电刺激系统在机械通气患者应用的初始评估
2750
8
文献学习12 | 肌松剂在ARDS中的早期应用
2443
9
文献学习23 | 利奈唑胺与万古霉素治疗ICU患者气管导管MRSA生物膜的疗效比较
2411
10
ARDS免疫精准诊断和治疗之困惑、挑战和策略
2145


友情链接
联系我们
 公众号
公众号
 客服微信
客服微信